2015-07-28 17:29:19
这一篇主要看看布局过程
一、布局过程肯定要不可避免的涉及到layout()和onLayout()方法,这两个方法都是定义在View.java中,源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Assign a size and position to a view and all of its 3 * descendants 4 * 5 *This is the second phase of the layout mechanism. 6 * (The first is measuring). In this phase, each parent calls 7 * layout on all of its children to position them. 8 * This is typically done using the child measurements 9 * that were stored in the measure pass().
10 *11 *Derived classes should not override this method.12 * Derived classes with children should override13 * onLayout. In that method, they should14 * call layout on each of their children.
15 *16 * @param l Left position, relative to parent17 * @param t Top position, relative to parent18 * @param r Right position, relative to parent19 * @param b Bottom position, relative to parent20 */21 @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})22 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {23 if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {24 onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);25 mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;26 }27 28 int oldL = mLeft;29 int oldT = mTop;30 int oldB = mBottom;31 int oldR = mRight;32 33 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?34 setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);35 if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {36 /// M: Monitor onLayout time if longer than 3s print log.37 long logTime = System.currentTimeMillis();38 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);39 long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();40 if (nowTime - logTime > DBG_TIMEOUT_VALUE) {41 Xlog.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "[ANR Warning]onLayout time too long, this =" + this + "time =" + (nowTime - logTime));42 }43 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;44 45 ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;46 if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {47 ArrayListlistenersCopy =48 (ArrayList )li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();49 int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();50 for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {51 listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);52 }53 }54 }55 56 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;57 mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;58 }59 60 /**61 * Called from layout when this view should62 * assign a size and position to each of its children.63 *64 * Derived classes with children should override65 * this method and call layout on each of66 * their children.67 * @param changed This is a new size or position for this view68 * @param left Left position, relative to parent69 * @param top Top position, relative to parent70 * @param right Right position, relative to parent71 * @param bottom Bottom position, relative to parent72 */73 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {74 }
简单的翻译一下layout()方法的那段注释哈~E文不好~
“指定一个view以及它的所有子孙节点的大小和位置,这是布局机制的第二阶段(第一阶段是测量),在这一阶段,父view调用所有子view的layout()方法以确定他们所在的位置,通常是使用子View存储的自身的尺寸。派生类不应该重写此方法,应该重写onLayout()方法,在派生类重写的onLayout()方法中,应该调用每一个子View的layout方法。”啰嗦一句,int l, int t, int r, int b都是相对于父节点的坐标值。
注意layout方法中的红色代码,调用了onLayout。而onLayout在view中实现为空。现在来看看ViewGroup中的这两个方法。
1 /** 2 * { @inheritDoc} 3 */ 4 @Override 5 public final void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { 6 if (!mSuppressLayout && (mTransition == null || !mTransition.isChangingLayout())) { 7 if (mTransition != null) { 8 mTransition.layoutChange(this); 9 }10 super.layout(l, t, r, b);11 } else {12 // record the fact that we noop'd it; request layout when transition finishes13 mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = true;14 }15 }16 17 /**18 * { @inheritDoc}19 */20 @Override21 protected abstract void onLayout(boolean changed,22 int l, int t, int r, int b); 在ViewGroup的layout方法中,mSuppressLayout用来控制是否禁止调用layout(),该值由如下方法来控制:
1 /** 2 * Tells this ViewGroup to suppress all layout() calls until layout 3 * suppression is disabled with a later call to suppressLayout(false). 4 * When layout suppression is disabled, a requestLayout() call is sent 5 * if layout() was attempted while layout was being suppressed. 6 * 7 * @hide 8 */ 9 public void suppressLayout(boolean suppress) {10 mSuppressLayout = suppress;11 if (!suppress) {12 if (mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed) {13 requestLayout();14 mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = false;15 }16 }17 } 这个方法不是对外公开的,所以不了解它也行。可以简单地理解ViewGroup的layout方法,它直接调用了父类View的layout()方法即可。至于onLayout方法,竟然被搞成了abstract的,这是逼着ViewGroup的子类必须得去实现啊~当然了,你必须得实现啊,你作为一个容器类,如何摆放你的子孙控件,是你义不容辞的责任啊。
至此我们已经明白了几点:
1. 派生类不需要重写layout(),而应该重写onLayout()方法,因为在layout()方法中就调用了onLayout()。
2. 在重写onLayout()方法时,我们需要显式的调用每一个childView的layout方法,把它摆放在合适的位置上。前提是在调用之前,得先计算好该childView的坐标。
3. 如果直接继承自View,那么可以不用重写onLayout()方法,比如ImageView、ImageButton等都没有重写该方法,所以不重写这个方法对于自定义View影响不大,至于TextView比较特殊,它重写了该方法,如下:


1 @Override 2 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { 3 super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); 4 if (mDeferScroll >= 0) { 5 int curs = mDeferScroll; 6 mDeferScroll = -1; 7 bringPointIntoView(Math.min(curs, mText.length())); 8 } 9 } 10 11 /** 12 * Move the point, specified by the offset, into the view if it is needed. 13 * This has to be called after layout. Returns true if anything changed. 14 */ 15 public boolean bringPointIntoView(int offset) { 16 if (isLayoutRequested()) { 17 mDeferScroll = offset; 18 return false; 19 } 20 boolean changed = false; 21 22 Layout layout = isShowingHint() ? mHintLayout: mLayout; 23 24 if (layout == null) return changed; 25 26 int line = layout.getLineForOffset(offset); 27 28 int grav; 29 30 switch (layout.getParagraphAlignment(line)) { 31 case ALIGN_LEFT: 32 grav = 1; 33 break; 34 case ALIGN_RIGHT: 35 grav = -1; 36 break; 37 case ALIGN_NORMAL: 38 grav = layout.getParagraphDirection(line); 39 break; 40 case ALIGN_OPPOSITE: 41 grav = -layout.getParagraphDirection(line); 42 break; 43 case ALIGN_CENTER: 44 default: 45 grav = 0; 46 break; 47 } 48 49 // We only want to clamp the cursor to fit within the layout width 50 // in left-to-right modes, because in a right to left alignment, 51 // we want to scroll to keep the line-right on the screen, as other 52 // lines are likely to have text flush with the right margin, which 53 // we want to keep visible. 54 // A better long-term solution would probably be to measure both 55 // the full line and a blank-trimmed version, and, for example, use 56 // the latter measurement for centering and right alignment, but for 57 // the time being we only implement the cursor clamping in left to 58 // right where it is most likely to be annoying. 59 final boolean clamped = grav > 0; 60 // FIXME: Is it okay to truncate this, or should we round? 61 final int x = (int)layout.getPrimaryHorizontal(offset, clamped); 62 final int top = layout.getLineTop(line); 63 final int bottom = layout.getLineTop(line + 1); 64 65 int left = (int) FloatMath.floor(layout.getLineLeft(line)); 66 int right = (int) FloatMath.ceil(layout.getLineRight(line)); 67 int ht = layout.getHeight(); 68 69 int hspace = mRight - mLeft - getCompoundPaddingLeft() - getCompoundPaddingRight(); 70 int vspace = mBottom - mTop - getExtendedPaddingTop() - getExtendedPaddingBottom(); 71 if (!mHorizontallyScrolling && right - left > hspace && right > x) { 72 // If cursor has been clamped, make sure we don't scroll. 73 right = Math.max(x, left + hspace); 74 } 75 76 int hslack = (bottom - top) / 2; 77 int vslack = hslack; 78 79 if (vslack > vspace / 4) 80 vslack = vspace / 4; 81 if (hslack > hspace / 4) 82 hslack = hspace / 4; 83 84 int hs = mScrollX; 85 int vs = mScrollY; 86 87 if (top - vs < vslack) 88 vs = top - vslack; 89 if (bottom - vs > vspace - vslack) 90 vs = bottom - (vspace - vslack); 91 if (ht - vs < vspace) 92 vs = ht - vspace; 93 if (0 - vs > 0) 94 vs = 0; 95 96 if (grav != 0) { 97 if (x - hs < hslack) { 98 hs = x - hslack; 99 }100 if (x - hs > hspace - hslack) {101 hs = x - (hspace - hslack);102 }103 }104 105 if (grav < 0) {106 if (left - hs > 0)107 hs = left;108 if (right - hs < hspace)109 hs = right - hspace;110 } else if (grav > 0) {111 if (right - hs < hspace)112 hs = right - hspace;113 if (left - hs > 0)114 hs = left;115 } else /* grav == 0 */ {116 if (right - left <= hspace) {117 /*118 * If the entire text fits, center it exactly.119 */120 hs = left - (hspace - (right - left)) / 2;121 } else if (x > right - hslack) {122 /*123 * If we are near the right edge, keep the right edge124 * at the edge of the view.125 */126 hs = right - hspace;127 } else if (x < left + hslack) {128 /*129 * If we are near the left edge, keep the left edge130 * at the edge of the view.131 */132 hs = left;133 } else if (left > hs) {134 /*135 * Is there whitespace visible at the left? Fix it if so.136 */137 hs = left;138 } else if (right < hs + hspace) {139 /*140 * Is there whitespace visible at the right? Fix it if so.141 */142 hs = right - hspace;143 } else {144 /*145 * Otherwise, float as needed.146 */147 if (x - hs < hslack) {148 hs = x - hslack;149 }150 if (x - hs > hspace - hslack) {151 hs = x - (hspace - hslack);152 }153 }154 }155 156 if (hs != mScrollX || vs != mScrollY) {157 if (mScroller == null) {158 scrollTo(hs, vs);159 } else {160 long duration = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis() - mLastScroll;161 int dx = hs - mScrollX;162 int dy = vs - mScrollY;163 164 if (duration > ANIMATED_SCROLL_GAP) {165 mScroller.startScroll(mScrollX, mScrollY, dx, dy);166 awakenScrollBars(mScroller.getDuration());167 invalidate();168 } else {169 if (!mScroller.isFinished()) {170 mScroller.abortAnimation();171 }172 173 scrollBy(dx, dy);174 }175 176 mLastScroll = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();177 }178 179 changed = true;180 }181 182 if (isFocused()) {183 // This offsets because getInterestingRect() is in terms of viewport coordinates, but184 // requestRectangleOnScreen() is in terms of content coordinates.185 186 // The offsets here are to ensure the rectangle we are using is187 // within our view bounds, in case the cursor is on the far left188 // or right. If it isn't withing the bounds, then this request189 // will be ignored.190 if (mTempRect == null) mTempRect = new Rect();191 mTempRect.set(x - 2, top, x + 2, bottom);192 getInterestingRect(mTempRect, line);193 ///M: ALPS00605613 requestRectangleOnScreen() will return error result if setting the mTempRect to mScrollX, mScrollY194 //mTempRect.offset(mScrollX, mScrollY);195 196 if (requestRectangleOnScreen(mTempRect)) {197 changed = true;198 }199 }200 201 return changed;202 } 有点没看明白bringPointIntoView方法的作用是什么,还得再研究。不过这不影响我们分析布局过程。
二、结合自己写的一个小Demo继续分析,代码如下:
MyLinear2.java
1 public class MyLinear2 extends ViewGroup { 2 private static final String TAG = "David_MyLinear2"; 3 4 public MyLinear2(Context context) { 5 super(context); 6 } 7 8 public MyLinear2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 9 super(context, attrs); 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 14 int count = getChildCount(); 15 int cWidth = 0; 16 int cHeight = 0; 17 int top = 0; 18 MarginLayoutParams params = null; 19 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "l = " + l); 20 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "t = " + t); 21 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "r = " + r); 22 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "b = " + b); 23 24 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 25 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "====================i = " + i); 26 View childView = getChildAt(i); 27 cWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 28 cHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 29 params = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams(); 30 31 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.height = " + params.height); 32 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.width = " + params.width); 33 int leftMargin = params.leftMargin; 34 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "leftMargin = " + leftMargin); 35 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.rightMargin = " + params.rightMargin); 36 /*Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "cWidth = " + cWidth); 37 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "cHeight = " + cHeight); 38 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "getWidth() = " + childView.getWidth()); 39 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "getHeight() = " + childView.getHeight());*/ 40 int cl = 0, ct = 0, cr = 0, cb = 0; 41 cl = leftMargin; 42 cr = cl + cWidth; 43 ct = top; 44 cb = cHeight + ct; 45 /*Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "cr = " + cr); 46 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "ct = " + ct); 47 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "cb = " + cb); 48 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "top = " + top);*/ 49 childView.layout(cl, ct, cr, cb); 50 top += cHeight; 51 } 52 } 53 54 @Override 55 public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { 56 Log.e(TAG, "generateLayoutParams attrs"); 57 return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() { 62 Log.e(TAG, "generateDefaultLayoutParams"); 63 return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 protected boolean checkLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) { 68 return super.checkLayoutParams(p); 69 } 70 71 @Override 72 protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) { 73 Log.e(TAG, "generateLayoutParams p"); 74 return new MarginLayoutParams(p); 75 } 76 77 @Override 78 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 79 int measuredHeight = measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec); 80 int measuredWidth = measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec); 81 Log.e(TAG, "onMeasure measuredHeight = " + measuredHeight); 82 Log.e(TAG, "onMeasure measuredWidth = " + measuredWidth); 83 setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight); 84 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 85 } 86 87 private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) { 88 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); 89 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); 90 91 int result = 500; 92 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ 93 result = specSize; 94 } else if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){ 95 result = specSize; 96 } 97 return result; 98 } 99 100 private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {101 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);102 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);103 104 int result = 100;105 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){106 result = specSize;107 } else if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){108 result = specSize;109 }110 return result;111 }112 } MyLinear2时模仿纵向布局的LinearLayout。
MyTextView.java
1 public class MyTextView extends View { 2 private static final String TAG = "David___MyTextView"; 3 4 public MyTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 5 super(context, attrs); 6 } 7 8 public MyTextView(Context context) { 9 super(context);10 }11 12 @Override13 protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {14 super.onDraw(canvas);15 Paint paint = new Paint();16 paint.setTextSize(22);17 paint.setTextAlign(Align.CENTER);18 Log.e(TAG, "onDraw getTop() = " + getTop());19 Log.e(TAG, "onDraw getLeft() = " + getLeft());20 canvas.drawText("nihao ----", getTop(), getLeft(), paint);21 }22 23 @Override24 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {25 Log.e(TAG, "onLayout left = " + left);26 Log.e(TAG, "onLayout top = " + top);27 Log.e(TAG, "onLayout right = " + right);28 Log.e(TAG, "onLayout bottom = " + bottom);29 //super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);30 }31 32 @Override33 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {34 int measuredHeight = measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec);35 int measuredWidth = measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec);36 Log.e(TAG, "onMeasure measuredHeight = " + measuredHeight);37 Log.e(TAG, "onMeasure measuredWidth = " + measuredWidth);38 setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);39 }40 41 private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) {42 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);43 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);44 45 int result = 500;46 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){47 result = specSize;48 } else if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){49 result = specSize;50 }51 return result;52 }53 54 private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {55 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);56 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);57 58 int result = 500;59 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){60 result = specSize;61 } else if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){62 result = specSize;63 }64 return result;65 }66 } 这是一个简易的View,先不要关心onDraw()方法。布局文件如下:
16 7 14 15 23 24 25 30 31
OK,运行打印的日志如下:
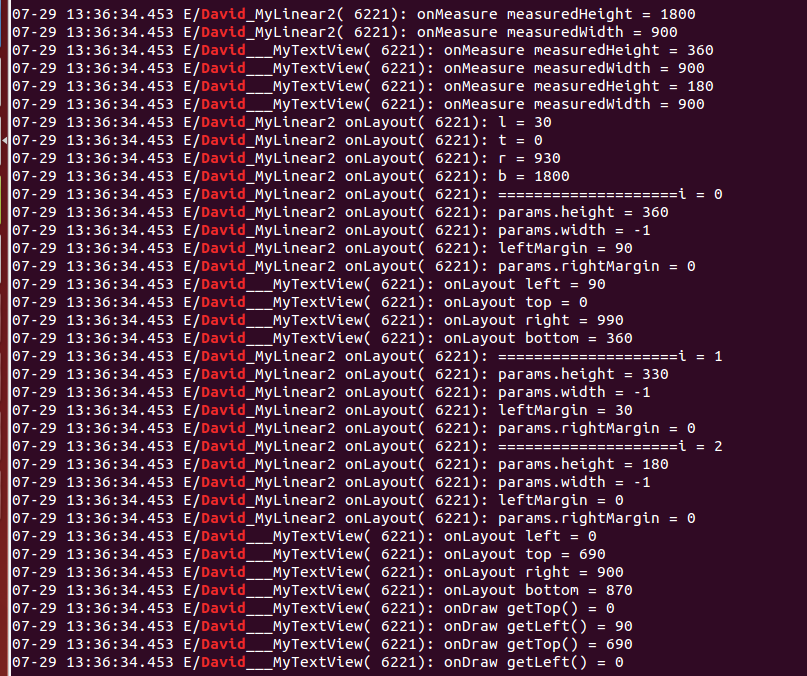
这段日志其实是会被打印好几遍的,我只截取了完整的一次日志。从日志可以看出,首先执行的是测量过程,这个之前分析过了,请参考http://www.cnblogs.com/wlrhnh/p/4680636.html。然后才是布局过程,由于我们在MyLinear2的onLayout()中显式调用childView的layout()方法,代码如下:
1 @Override 2 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 3 int count = getChildCount(); 4 int cWidth = 0; 5 int cHeight = 0; 6 int top = 0; 7 MarginLayoutParams params = null; 8 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "l = " + l); 9 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "t = " + t);10 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "r = " + r);11 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "b = " + b);12 13 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {14 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "====================i = " + i);15 View childView = getChildAt(i);16 cWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();17 cHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();18 params = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();19 20 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.height = " + params.height);21 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.width = " + params.width);22 int leftMargin = params.leftMargin;23 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "leftMargin = " + leftMargin);24 Log.e(TAG + " onLayout", "params.rightMargin = " + params.rightMargin);25 int cl = 0, ct = 0, cr = 0, cb = 0;26 cl = leftMargin;27 cr = cl + cWidth;28 ct = top;29 cb = cHeight + ct;30 childView.layout(cl, ct, cr, cb);31 top += cHeight;32 }33 } 所以日志中显示:先调用了ViewGroup的onLayout,然后遍历每一个childView,取出它们已经计算好的坐标值,按照ViewGroup的既定布局策略,给childView布局,调用他们的layout()方法,进而调用了onLayout()。而很多继承自View的组件,比如ImageView等,由于没有实现onLayout()方法,那么其实只调用了View的layout()和View的空实现的onLayout()方法。当然了,我在MyTextView中重写onLayout()只是为了打印日志而已,并没有做什么实际操作。在日志的最后,打印了onDraw()方法,可见,先测量、后布局、最后才统一draw,并不是布局完一个就draw一个。而且我发现一个有意思的现象,那就是如果你的父控件拥有的space不足以显示所有的子View,那么不能显示出来的子View的onDraw方法是不会被调用的,这点好理解~
三、关于LayoutParams
注意上面的一行红色代码,每个childView都有LayoutParams,而且可以强转为MarginLayoutParams呢?注意看这几行代码:
1 @Override 2 public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { 3 Log.e(TAG, "generateLayoutParams attrs"); 4 return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() { 9 Log.e(TAG, "generateDefaultLayoutParams");10 return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);11 }12 13 @Override14 protected boolean checkLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {15 return super.checkLayoutParams(p);16 }17 18 @Override19 protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {20 Log.e(TAG, "generateLayoutParams p");21 return new MarginLayoutParams(p);22 } 看一下日志:
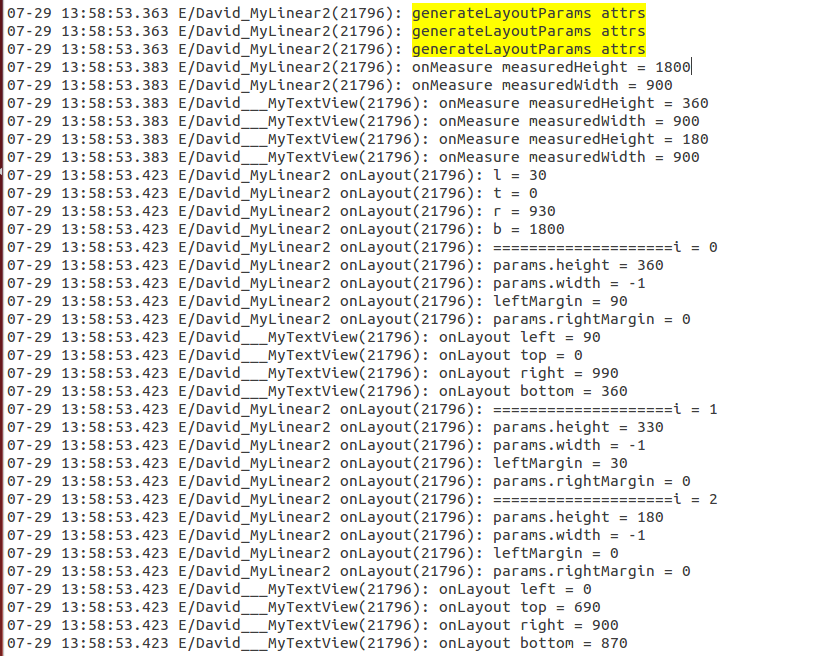
看黄色部分日志,主要执行了generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)方法,而且是先于测量过程执行的,这个方法我们有自己的实现,具体的请参考http://www.cnblogs.com/wlrhnh/p/4683542.html
简单的总结一下布局过程:
Android View绘制系统首先取到Activity布局的根View,当然这一般是一个ViewGroup了。先测量,后布局。布局的时候调用ViewGroup子类比如MyLinear2的layout()方法,由于ViewGroup强制子类实现onLayout()方法,所以会调到MyLinear2的onLayout()方法,在这个方法中,需要遍历子View,按照布局策略,计算每一个子View的坐标,然后将它放在合适的位置上。至于继承自View的子类,则不需要实现onLayout,毕竟onLayout的作是布局,这是容器类该干的事情。而子View要做的就是根据父View在指定给自己的空间中draw。
通过以上三篇文章,想必应该对Android系统测量、布局View的流程有了一个大概的了解,这是一条主线。当然了,这里面涉及到的细节其实有很多,最好的办法是自己去看源码喽~
项目代码和View.java ViewGroup.java LinearLayout.java Button.java等源码请下载
后记:分析完三步骤之后觉得不过瘾,想起网上有人写过这样的布局,就顺手写了个,抄袭人家的创意了,但是代码是自己的写的~

1 public class MyLinear1 extends ViewGroup { 2 private static final String TAG = "David_MyLinear1"; 3 4 public MyLinear1(Context context) { 5 super(context); 6 } 7 8 public MyLinear1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 9 super(context, attrs); 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 14 int measuredHeightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); 15 int measuredWidthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); 16 17 int measuredHeightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); 18 int measuredWidthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); 19 20 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 21 22 int lHeight = 0, rHeight = 0; 23 int tWidth = 0, bWidth = 0; 24 25 View childView = null; 26 MarginLayoutParams params = null; 27 for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { 28 childView = getChildAt(i); 29 params = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams(); 30 31 switch (i) { 32 case 0: 33 lHeight += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 34 tWidth += childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 35 break; 36 case 1: 37 rHeight += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 38 tWidth += childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 39 break; 40 case 2: 41 lHeight += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 42 bWidth += childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 43 break; 44 case 3: 45 rHeight += childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 46 bWidth += childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 47 break; 48 49 default: 50 break; 51 } 52 } 53 54 int realHeightSize = Math.max(lHeight, rHeight); 55 int realWidthSize = Math.max(bWidth, tWidth); 56 int h = measuredHeightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? measuredHeightSize : realHeightSize; 57 int w = measuredWidthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? measuredWidthSize : realWidthSize; 58 setMeasuredDimension(w, h); 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 63 int realLeft = 0; 64 int realTop = 0; 65 int realRight = 0; 66 int realBottom = 0; 67 int count = getChildCount(); 68 69 View childView = null; 70 MarginLayoutParams params = null; 71 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 72 Log.e(TAG, "------------------------- i = " + i); 73 childView = getChildAt(i); 74 params = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams(); 75 Log.d(TAG, "childView.getMeasuredWidth() = " + childView.getMeasuredWidth()); 76 Log.d(TAG, "childView.getMeasuredHeight() = " + childView.getMeasuredHeight()); 77 switch (i) { 78 case 0: 79 realLeft = l; 80 realTop = t; 81 realRight = realLeft + childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 82 realBottom = realTop + childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 83 break; 84 case 1: 85 realLeft = r - childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 86 realTop = t; 87 realRight = realLeft + childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 88 realBottom = realTop + childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 89 break; 90 case 2: 91 realLeft = l; 92 realTop = b - childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 93 realRight = realLeft + childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 94 realBottom = realTop + childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 95 break; 96 case 3: 97 realLeft = r - childView.getMeasuredWidth(); 98 realTop = b - childView.getMeasuredHeight(); 99 realRight = realLeft + childView.getMeasuredWidth();100 realBottom = realTop + childView.getMeasuredHeight();101 break;102 103 default:104 break;105 }106 childView.layout(realLeft, realTop, realRight, realBottom);107 }108 }109 110 @Override111 public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {112 return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);113 }114 }
代码随手写的,有些问题考虑的还不够周全,各位自己完善吧~而且没有做注释,但是相信看完这三篇文章,不需要看注释了吧~